スマートカードのシステム - 背景技術 段落5 #0032
【背景技術】段落5
現在、スマートカードを採用している多くのシステムでは、利用者数が非常に増大している。たとえば、電子バンキングシステムにおいて、相当数の顧客が現金自動預け払い機を日々アクセスすると予想できるだろう。したがって、判読機の費用は十分な取引数を通じて償却されることは、サービスの提供者にとって容易に理にかなうものである。
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1st paragraph
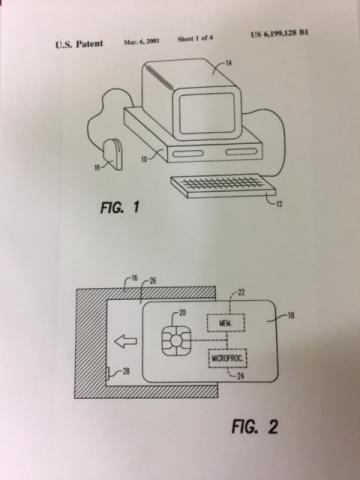
The use of secure smart cards that provide information specific to an individual is becoming more prevalent in a number of different types of situations. Examples of such include electronic commerce, security access control and health care record maintenance. Each system which employs smart cards contains two fundamental components, namely the smart cards themselves and an interface device, commonly known as a reader. The smart cards are carried by the users of the system, and include a memory which stores information that is pertinent to the user's interaction with the system. In an electronic commerce system, for example, each smart card may contain the balance in an account maintained by the user, as well as details of account transactions. More recently, the smart cards also include microprocessors, which provide for an increased level of security over the information stored in the cards. The incorporation of microprocessors into the cards also enhances their flexibility, for instance by facilitating the storage of executable programs in the cards that can be used to provide expanded functionality.
United States Patent 6,199,128 Inventors: Sarat; Jean-Marc (Belmont, CA)
【背景技術】段落5
現在、スマートカードを採用している多くのシステムでは、利用者数が非常に増大している。たとえば、電子バンキングシステムにおいて、相当数の顧客が現金自動預け払い機を日々アクセスすると予想できるだろう。したがって、判読機の費用は十分な取引数を通じて償却されることは、サービスの提供者にとって容易に理にかなうものである。
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 5th paragraph
In many systems which currently employ smart cards, the number of users can be quite large. For example, in an electronic banking system, a considerable number of customers might be expected to access an automated teller machine each day. Consequently, the cost of the reader is amortized over a sufficient number of transactions that it can be readily justified by the provider of the services.
United States Patent 6,199,128 Inventors: Sarat; Jean-Marc (Belmont, CA)
【背景技術】段落4
公開標準を遵守する必要があるため、従来のスマートカード判読機を比較的高い価格の機器として製造する。たとえば、ISO標準は、電源投入手続きの間に特定のシーケンスで予め設定された時刻に、異なる各信号がスマートカード上の5つの指定接点を用いることを要件とする。その結果、判読機はこれら信号のアプリケーションおよびタイミングを監視する制御部を有さなければならい、それにより費用が追加される。
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 4th paragraph
Due to the need to comply with the published standards, a conventional card reader can turn out to be a relatively expensive item of equipment. For instance, the ISO standard requires that different respective signals be applied to the five designated contacts on the card in a specific sequence at predetermined times during the power-up procedure. As a result, the reader must include a controller which supervises the application and timing of these signals, thereby adding to its cost.
【背景技術】段落3
異なる製造業者のスマートカードと判読機をたがいに互換性ありを可能するために、標準仕様のセットが開発された。スマートカードと判読機に適用される標準規格の1つがISO7816であり国際標準化機構によって公布された。この標準は、スマートカードの外面上における電気的接点の位置に対する仕様を定め、さらにそれぞれの接点で存在する電気的信号の機能を定めている。この点に関して、標準では最大で8個の電気的接点を供している。けれども、特定の信号についてはこれら接点のうち5個のみが定義されてる。標準では電源投入、初期化、判読機にスマートカードが最初に挿入された場合に実行する手続き、スマートカードと判読機の間で通信するプロトコルも含む。
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 3rd paragraph
【背景技術】段落2
判読機は、スマートカードの中に記憶された情報をアクセスするのに、安全な方法でスマートカードと通信する。系の1つの型において、スマートカードは判読機のスロットの中に挿入され、スマートカードの外面上に対応する接触ピンとかみ合わせて、判読機内で電気的接点をもたらす。かみ合った接触ピンは判読機内のマイクロコントローラーをメモリと通信をできるようにし、かつスマートカード内のマイクロプロセッサと通信を可能にする。一般的に、判読機が組み込まれる系の周辺装置に判読機は接続され、判読機は系の特定の型と連動する。たとえば、セキュリティシステムでは、判読機は扉を開けることを可能にする電子錠へと接続されるだろう。銀行システムにおいて、判読機は現金自動預け払い機内に組み込みできるだろう。
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 2nd paragraph
【背景技術】段落1
個人向けに特定の情報を供するスマートカードの安全な使用はさまざまな形の局面で広く行き渡っている。そのような実例には、電子商取引、安全アクセス管理および健康管理記録保全がある。スマートカードを採用するそれぞれの系は2つの基本的な構成要素を含む、すなわち該スマートカードとインターフェース装置で、一般に判読機として知られている。スマートカードは対応する系の利用者により携帯され、かつ対応する系と利用者の相互作用がぴったりと当てはまる情報を記憶するメモリを有する。電子商取引系において、たとえば、それぞれスマートカードには口座取引の詳細と同様に、利用者により管理維持された預金残高を含むであろう。より最近では、マイクロプロセッサの内装も有し、スマートカードの中に記憶された情報に対して従来にも増して安全性を提供する。スマートカードへのマイクロプロセッサの組込みはスマートカードの柔軟性もまた高める、たとえばスマートカードに実行可能プログラムの記憶機構を具備することにより機能拡張を供する使用が可能となる。